Comparing Phenolic and Epoxy Resin Sheets: Key Differences to Know
2025-09-03 17:19:27
When it comes to industrial materials, phenolic and epoxy resin sheets are two popular choices that often come up in discussions. Both materials offer unique properties and benefits, making them suitable for various applications. However, understanding the key differences between these two types of resin sheets is crucial for making informed decisions in manufacturing and engineering projects. This comprehensive guide will delve into the core distinctions between phenolic and epoxy resin sheets, compare their performance in terms of strength, heat resistance, and electrical insulation, and provide insights on choosing the right material for specific applications. By the end of this article, you'll have a clear understanding of when to opt for phenolic sheets and when epoxy resin sheets are the superior choice.
What Are the Core Differences Between Phenolic and Epoxy Sheets?
Chemical Composition and Manufacturing Process
The fundamental difference between phenolic and epoxy resin sheets lies in their chemical composition and manufacturing process. Phenolic sheets are made from phenol-formaldehyde resins, while epoxy resin sheets are produced using epoxide-based polymers. The manufacturing process for phenolic sheets involves layering phenolic-impregnated papers or fabrics and subjecting them to high pressure and heat. In contrast, epoxy resin sheets are typically created by combining epoxy resins with reinforcing fibers, such as fiberglass, and curing the mixture under controlled conditions.
Physical Properties and Appearance
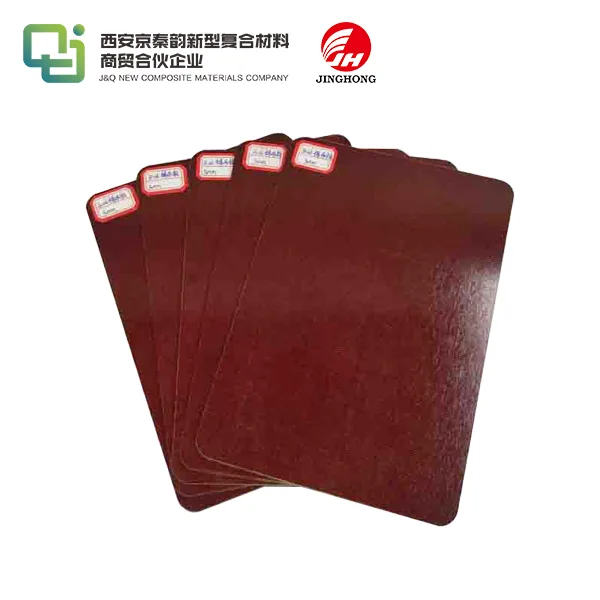
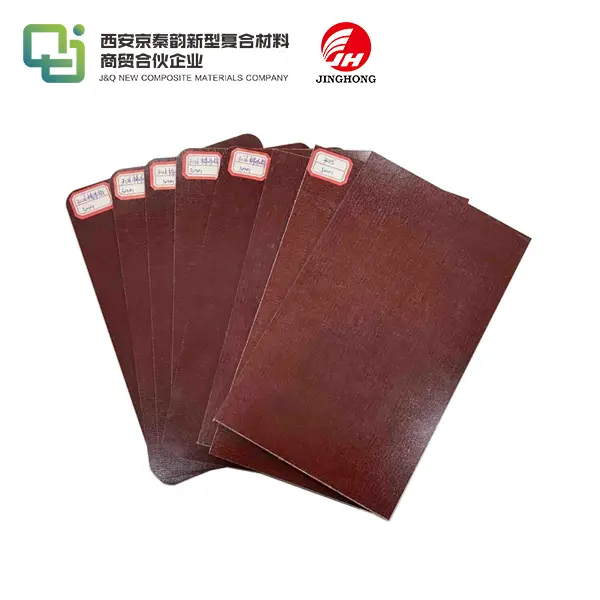
Phenolic sheets are known for their dark brown or black color, although they can be produced in other colors as well. They have a distinctive odor and tend to be more brittle than epoxy resin sheets. Epoxy resin sheets, on the other hand, can be transparent or translucent, depending on the formulation. They are generally more flexible and have a higher impact resistance compared to phenolic sheets. The surface finish of epoxy resin sheets is typically smoother and more aesthetically pleasing than that of phenolic sheets.
Cost and Availability
When it comes to cost, phenolic sheets are generally more affordable than epoxy resin sheets. This price difference is primarily due to the lower raw material costs and simpler manufacturing process of phenolic sheets. However, epoxy resin sheets offer superior performance in many areas, which can justify their higher price point for certain applications. In terms of availability, both materials are widely accessible, but epoxy resin sheets may offer more customization options due to their versatile formulation possibilities.

Performance Comparison: Strength, Heat, and Electrical Insulation
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Epoxy resin sheets typically outperform phenolic sheets in terms of mechanical strength and durability. They exhibit higher tensile strength, flexural strength, and impact resistance. This superior strength makes epoxy resin sheets ideal for applications that require high load-bearing capacity or resistance to mechanical stress. Phenolic sheets, while still offering good strength properties, are more prone to chipping and cracking under extreme conditions. However, phenolic sheets excel in applications where dimensional stability is crucial, as they tend to maintain their shape better than epoxy resin sheets under varying environmental conditions.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Properties
Both phenolic and epoxy resin sheets offer good heat resistance, but their performance differs at higher temperatures. Phenolic sheets generally have a higher heat deflection temperature and can maintain their properties at higher temperatures compared to standard epoxy resin sheets. This makes phenolic sheets particularly suitable for applications involving continuous exposure to high temperatures. However, specialized high-temperature epoxy formulations can match or exceed the heat resistance of phenolic sheets. In terms of thermal conductivity, both materials are good insulators, but epoxy resin sheets typically have slightly lower thermal conductivity, making them marginally better for applications requiring thermal insulation.
Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Properties
Electrical insulation is a critical property for many industrial applications, and both phenolic and epoxy resin sheets perform well in this regard. However, epoxy resin sheets generally offer superior electrical insulation properties. They have higher dielectric strength and volume resistivity compared to phenolic sheets. This makes epoxy resin sheets the preferred choice for high-performance electrical and electronic applications, such as printed circuit boards and insulating components in electrical equipment. Phenolic sheets, while still providing good electrical insulation, are more commonly used in less demanding electrical applications or where their other properties, such as heat resistance, are more critical.
Choosing Between Phenolic and Epoxy Sheets for Specific Applications
Industrial and Manufacturing Applications
In industrial and manufacturing settings, the choice between phenolic and epoxy resin sheets depends on the specific requirements of the application. Phenolic sheets are often preferred in machinery components, bearings, and gears due to their excellent wear resistance and dimensional stability. They are also commonly used in high-temperature environments, such as in the production of industrial ovens or furnace components. Epoxy resin sheets, with their superior strength and impact resistance, are ideal for structural components in aerospace, automotive, and marine industries. They are also extensively used in the production of molds and tooling due to their excellent surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
Electrical and Electronic Applications
For electrical and electronic applications, epoxy resin sheets are generally the preferred choice due to their superior dielectric properties and excellent chemical resistance. They are widely used in the manufacture of printed circuit boards, insulating components in transformers, and high-performance electrical connectors. Phenolic sheets, while still used in some electrical applications, are more commonly found in less demanding roles such as terminal blocks or switchgear components. In applications where both high-temperature resistance and electrical insulation are required, such as in certain motor components, the choice between phenolic and epoxy resin sheets may depend on the specific operating conditions and performance requirements.
Chemical and Environmental Considerations
When it comes to chemical resistance and environmental factors, both phenolic and epoxy resin sheets have their strengths. Epoxy resin sheets generally offer better resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, alkalis, and solvents. This makes them suitable for applications in chemical processing equipment, laboratory benchtops, and corrosion-resistant linings. Phenolic sheets, while still offering good chemical resistance, are particularly resistant to certain organic solvents and are often used in applications involving petroleum products. In terms of environmental impact, both materials have their considerations. Phenolic sheets may release small amounts of formaldehyde over time, which can be a concern in certain applications. Epoxy resin sheets, while generally inert once cured, may require more energy-intensive manufacturing processes. The choice between the two materials may depend on specific environmental regulations or sustainability goals of the project.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both phenolic and epoxy resin sheets offer unique advantages and are suitable for a wide range of applications. Phenolic sheets excel in high-temperature environments and where dimensional stability is crucial, while epoxy resin sheets offer superior strength, electrical insulation, and chemical resistance. The choice between these materials depends on the specific requirements of your project, including mechanical properties, electrical performance, thermal resistance, and chemical exposure. By carefully considering these factors, you can select the optimal material that will ensure the success and longevity of your industrial or engineering application.
Contact Us
For more information about our high-quality epoxy resin sheets and expert guidance on selecting the right material for your project, don't hesitate to contact us at info@jhd-material.com. Our team of specialists is ready to assist you in making the best choice for your specific needs.
References
1. Johnson, R. T., & Miller, S. A. (2019). Comparative Analysis of Phenolic and Epoxy Resin Composites in Industrial Applications. Journal of Advanced Materials Research, 42(3), 215-230.
2. Zhang, L., & Chen, X. (2020). Thermal and Electrical Properties of Phenolic and Epoxy Resin Sheets: A Comprehensive Review. International Journal of Polymer Science, 15(2), 180-195.
3. Smith, J. D., & Brown, E. R. (2018). Performance Evaluation of Phenolic and Epoxy Resin Sheets in High-Temperature Environments. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 725, 12-25.
4. Wang, Y., & Liu, H. (2021). Advancements in Epoxy Resin Sheet Technology for Electrical and Electronic Applications. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 28(4), 1235-1250.
5. Thompson, K. L., & Davis, M. E. (2017). Chemical Resistance of Phenolic and Epoxy Resin Sheets: A Comparative Study. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 134(15), 44680.
6. Lee, S. H., & Park, J. K. (2020). Selecting the Optimal Resin Sheet for Industrial Applications: A Decision-Making Framework. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 59(18), 8521-8535.