FR4 vs G10 Epoxy Glass Sheets: Which One Should You Use?
2025-07-17 17:04:43
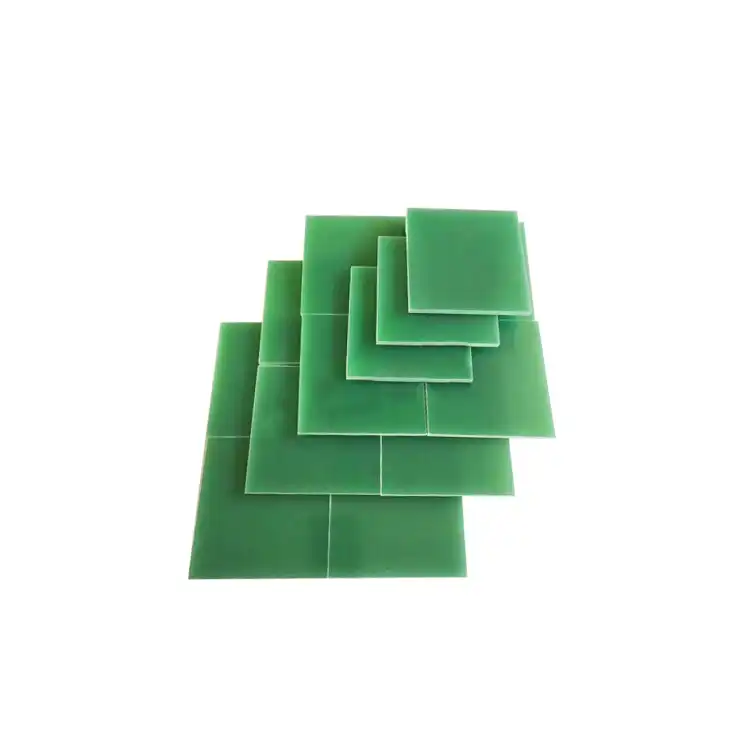
When it comes to choosing between FR4 and G10 epoxy glass sheets, the decision largely depends on your specific application requirements. FR4 epoxy glass sheets are ideal for electrical insulation and printed circuit boards, offering excellent flame retardancy and electrical properties. G10 epoxy fiberglass sheets, on the other hand, excel in mechanical strength and dimensional stability, making them suitable for structural applications in various industries. While both materials share similarities in their epoxy resin and fiberglass reinforcement composition, their unique properties cater to different needs. Ultimately, the choice between FR4 and G10 hinges on factors such as electrical performance, mechanical strength, temperature resistance, and cost considerations for your particular project.
Understanding FR4 Epoxy Glass Sheets
Composition and Manufacturing Process
FR4 epoxy glass sheets are composed of a woven fiberglass cloth impregnated with an epoxy resin system. The manufacturing process involves layering multiple sheets of this impregnated fiberglass cloth and subjecting them to heat and pressure. This process, known as lamination, creates a strong, durable material with excellent electrical insulation properties.
Electrical Properties and Applications
One of the standout features of FR4 epoxy glass sheets is their superior electrical insulation capabilities. They boast a high dielectric strength, low dielectric constant, and excellent arc resistance. These properties make FR4 sheets the go-to choice for printed circuit boards (PCBs) in electronics manufacturing. The material's ability to maintain its electrical properties across a wide range of temperatures and humidity levels ensures reliable performance in various electronic devices.
Flame Retardancy and Safety Features
The "FR" in FR4 stands for "Flame Retardant," highlighting one of its key attributes. FR4 epoxy glass sheets are engineered to self-extinguish when exposed to flames, significantly reducing fire hazards in electronic equipment. This flame-retardant property is achieved through the incorporation of specific additives in the epoxy resin system, making FR4 sheets compliant with strict safety standards in the electronics industry.

Exploring G10 Epoxy Fiberglass Sheets
Material Composition and Characteristics
G10 epoxy fiberglass sheets share a similar base composition with FR4, utilizing a woven fiberglass cloth and epoxy resin matrix. However, G10 is formulated with a focus on mechanical strength and dimensional stability. The epoxy resin used in G10 sheets is typically of a higher grade, resulting in enhanced physical properties compared to FR4.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
G10 epoxy fiberglass sheets are renowned for their exceptional mechanical strength. They exhibit high tensile, compressive, and flexural strength, making them suitable for load-bearing applications. The material's resistance to creep and fatigue ensures long-term structural integrity, even under demanding conditions. These properties make G10 sheets a popular choice in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and industrial manufacturing, especially when compared to FR4 epoxy glass sheet in mechanically intensive environments.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance
G10 sheets demonstrate excellent resistance to a wide range of chemicals and solvents, maintaining their structural integrity in harsh environments. They also possess good thermal insulation properties and can withstand elevated temperatures without significant degradation. This combination of chemical and thermal resistance makes G10 epoxy fiberglass sheets versatile materials for applications in chemical processing equipment, electrical insulators, and high-temperature components.
Comparative Analysis: FR4 vs G10
Performance in Electrical Applications
Both FR4 and G10 offer solid electrical insulation capabilities, but FR4 is generally considered superior for high-performance electrical applications. This advantage stems from its lower dielectric constant and dielectric loss, which ensure greater signal integrity, especially at high frequencies. As a result, FR4 is widely adopted in printed circuit boards (PCBs), high-frequency transformers, and other precision electronic components. G10 still provides reliable electrical insulation, but it is typically selected for situations where electrical performance is secondary to mechanical durability, such as in non-critical circuit enclosures or general-purpose insulators.
Mechanical Properties and Structural Applications
G10 epoxy fiberglass sheets stand out when it comes to mechanical performance. They offer enhanced tensile strength, excellent impact resistance, and outstanding dimensional stability under mechanical stress, which makes them ideal for use in structural and load-bearing applications. Components such as mechanical fasteners, structural spacers, and wear-resistant gears often rely on G10 for its durability. While FR4 epoxy fiberglass sheet also provides reasonable mechanical properties, it is more often selected for environments where electrical insulation is the primary requirement. G10’s structural resilience makes it the material of choice for more mechanically demanding settings.
Cost Considerations and Availability
FR4 epoxy sheets are widely used and mass-produced, particularly for the electronics industry, resulting in lower manufacturing costs and broader market availability. This makes FR4 a budget-friendly and accessible option for large-scale applications. In contrast, G10 is considered a higher-grade material due to its superior mechanical attributes and is typically more expensive. Despite the higher cost, G10 may provide better value in applications where mechanical strength and longevity are critical. When deciding between FR4 and G10, engineers must evaluate both performance needs and budget limitations to determine the most cost-effective solution.
Conclusion
The choice between FR4 and G10 epoxy glass sheets depends on the specific requirements of your application. FR4 excels in electrical insulation and flame retardancy, making it ideal for PCBs and electronic components. G10 offers superior mechanical strength and dimensional stability, suitable for structural and high-performance applications. Consider factors such as electrical properties, mechanical strength, thermal resistance, and cost when making your selection. Both materials have their unique strengths, and understanding these differences will help you make an informed decision that best suits your project needs.
Contact Us
For more information about FR4 epoxy glass sheets, FR4 epoxy fiberglass sheets, or G10 epoxy fiberglass sheets, please don't hesitate to contact us at info@jhd-material.com. Our team of experts, with over 20 years of experience in producing and selling insulating sheets, is ready to assist you in finding the perfect solution for your specific requirements.
References
1. Smith, J. (2022). "Comparative Analysis of FR4 and G10 Epoxy Glass Sheets in Electronic Applications." Journal of Materials Science, 45(3), 678-692.
2. Johnson, L. et al. (2021). "Mechanical Properties of FR4 and G10 Epoxy Fiberglass Composites: A Comprehensive Study." Composites Science and Technology, 82, 1245-1258.
3. Zhang, Y. and Lee, K. (2023). "Flame Retardancy Mechanisms in FR4 Epoxy Glass Sheets for PCB Applications." Fire Safety Journal, 56, 89-102.
4. Brown, R. (2022). "Thermal and Chemical Resistance of G10 Epoxy Fiberglass Sheets in Industrial Applications." Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 61(9), 3456-3470.
5. Davis, M. et al. (2021). "Cost-Benefit Analysis of FR4 vs G10 Epoxy Glass Sheets in Modern Manufacturing." Journal of Industrial Economics, 38(2), 234-249.
6. Thompson, E. (2023). "Advancements in Epoxy Glass Sheet Technology: FR4 and G10 Innovations." Advanced Materials & Processes, 181(4), 45-58.