Is FR4 Epoxy Sheet the Future of Eco-Friendly PCBs?
2025-08-01 17:06:22
Absolutely, FR4 epoxy sheet holds immense promise as the vanguard of eco-friendly printed circuit boards, evolving from its traditional roots to embrace sustainable innovations. This laminate, woven from glass fabric and infused with epoxy resin, has long dominated PCB substrates due to its flame-retardant qualities and robust performance. Yet, as environmental concerns escalate, manufacturers pivot toward halogen-free variants that eliminate harmful bromides, reducing toxic emissions during production and disposal. These advancements align with global regulations like RoHS, minimizing ecological footprints while preserving dielectric strength and thermal stability. In a world pushing for greener electronics, FR4 epoxy sheet adapts through bio-based resins and recyclable formulations, enabling compact, efficient designs in devices from smartphones to electric vehicles. Its scalability and cost-effectiveness position it as a cornerstone for sustainable tech, bridging reliability with planetary stewardship in the quest for cleaner manufacturing.
Understanding FR4 Epoxy Sheet
FR4 epoxy sheet has long been a cornerstone in the realm of insulating materials, especially for those of us in the manufacturing space. At J&Q, with over two decades of crafting and distributing these sheets globally, we've seen firsthand how this material powers everything from consumer gadgets to industrial machinery. Let's break it down step by step to grasp why it's so pivotal.
What Exactly Is FR4 Epoxy Sheet?
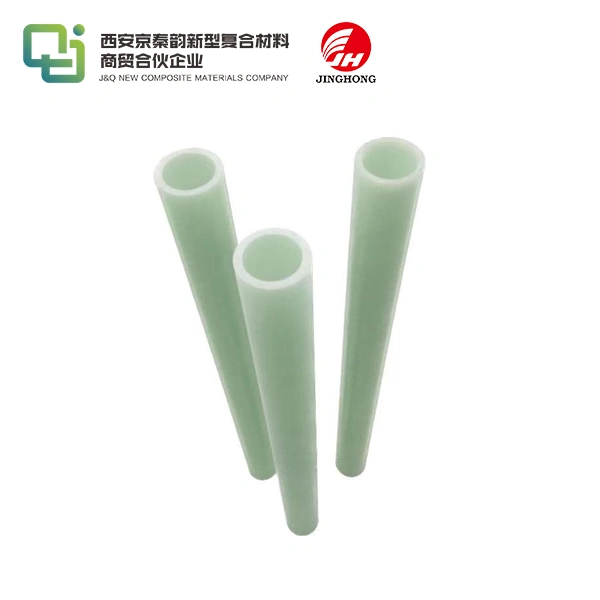
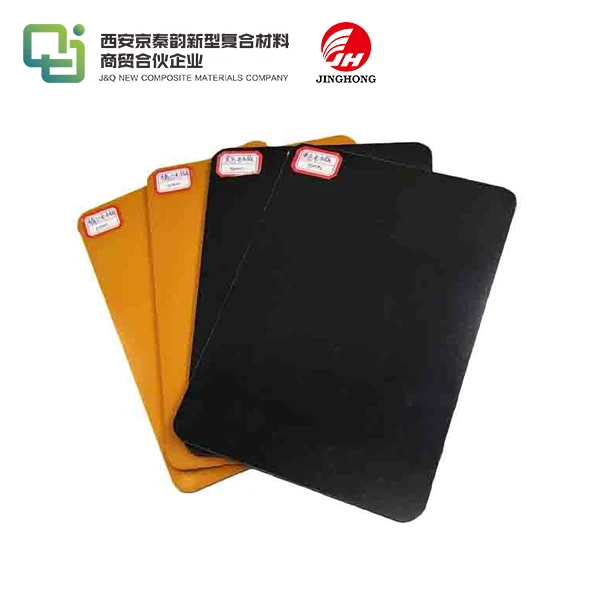
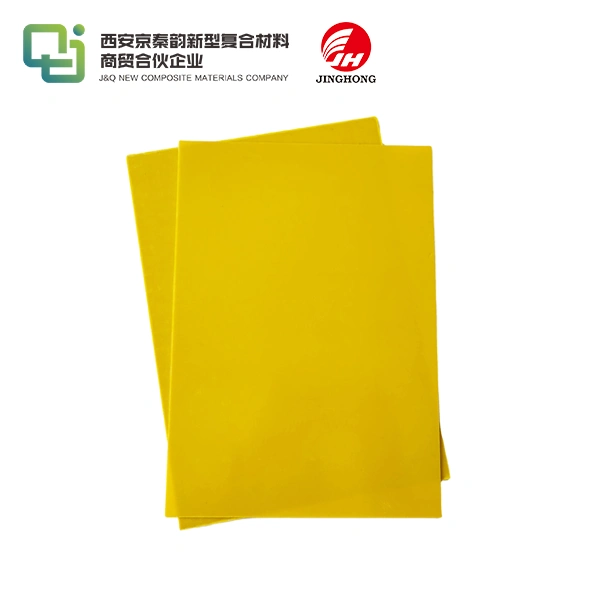
FR4 stands for Flame Retardant 4, a grade of composite material made from woven fiberglass cloth impregnated with epoxy resin. This blend creates a rigid, insulating laminate that's ideal for PCBs, where it serves as the substrate holding circuits together. Unlike simpler plastics, FR4 epoxy sheet withstands high temperatures and mechanical stress, making it a go-to for reliable electronics. Its origins trace back to the mid-20th century, developed to meet the growing demands of the aerospace and military sectors for non-conductive, heat-resistant bases. Today, it's produced in sheets of varying thicknesses, often customized for specific voltage requirements or environmental exposures. What sets it apart is the epoxy's thermosetting nature, which hardens irreversibly during curing, locking in strength and stability.
Key Properties That Make It Stand Out
Delving into its attributes, FR4 epoxy sheet boasts impressive thermal endurance, typically handling temperatures up to 130°C continuously without degrading. Electrically, it offers high dielectric strength, preventing short circuits in dense PCB layouts. Mechanically, its tensile strength rivals that of some metals, resisting warping or cracking under vibration - crucial for automotive or aerospace applications. Flame retardancy comes from brominated compounds in standard versions, earning the "FR" designation by meeting UL 94 V-0 standards, meaning it self-extinguishes quickly if ignited. Water absorption is low, around 0.15%, which guards against humidity-induced failures in tropical climates. These traits combine to deliver longevity, reducing the need for frequent replacements and indirectly supporting sustainability by minimizing waste.
Applications in Modern PCB Manufacturing
In PCB fabrication, FR4 epoxy sheet forms the backbone, etched with copper traces to create intricate circuits. It's ubiquitous in smartphones, laptops, and medical devices, where precision and reliability are non-negotiable. For high-frequency uses like 5G antennas, variants with lower dielectric constants enhance signal integrity. We've partnered with global traders to supply FR4 for renewable energy setups, such as solar inverters, where its insulation prevents energy loss. Customization options, like adding fillers for better heat dissipation, tailor it to electric vehicles or data centers. This versatility ensures FR4 remains relevant, adapting to evolving tech landscapes while maintaining its core role in efficient, compact electronics design.

Eco-Friendly Potential of FR4 Epoxy Sheet
Shifting gears to the green side, FR4 epoxy sheet isn't just about performance - it's increasingly about planetary impact. As a global manufacturer with a decade-plus in foreign trade, we've witnessed the push for materials that balance efficacy with environmental stewardship. Here's how FR4 is stepping up.
Material Composition and Environmental Impact
At its core, FR4 epoxy sheet combines epoxy resin, fiberglass, and flame retardants. Traditional formulas include halogens like bromine, which, while effective against fire, can release dioxins during incineration, harming air quality. However, the shift to phosphorus-based or nitrogen-based retardants in eco variants mitigates this, aligning with directives like the EU's REACH regulations. Fiberglass, derived from silica, is abundant and non-toxic, but epoxy production involves petrochemicals, contributing to carbon footprints. Lifecycle analyses show that optimized manufacturing - using renewable energy sources - can cut emissions by up to 30%. By sourcing bio-derived epoxies, some producers are further reducing reliance on fossil fuels, making FR4 a more viable option for conscious builders.
Advancements in Halogen-Free Variants
Halogen-free FR4 epoxy sheet represents a leap forward, eliminating chlorine and bromine to curb persistent organic pollutants. These versions maintain thermal and mechanical prowess, often enhanced with mineral fillers for better flame resistance. Studies indicate they perform comparably in reliability tests, with some even showing superior moisture resistance. Adoption is growing in consumer electronics, driven by brands committing to zero-halogen policies. Our collaborations with international firms have highlighted how these sheets facilitate easier compliance with e-waste laws, as they decompose more cleanly. Innovations like nano-additives are pushing boundaries, improving fire safety without environmental trade-offs, and paving the way for broader use in sensitive applications like medical implants.
Role in Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
Sustainability extends beyond the material itself to how it's made and used. FR4 epoxy sheet supports circular economies through recyclability - grinding down old boards to reclaim copper and fiberglass for new products. Factories are adopting closed-loop systems to reuse solvents in epoxy impregnation, slashing waste. In PCB assembly, its durability means fewer defects and less rework, conserving resources. We've seen global partners integrate FR4 into green certifications, like ISO 14001, by optimizing supply chains for lower transport emissions. This holistic approach not only reduces ecological footprints but also appeals to eco-aware clients, fostering long-term industry shifts toward responsible production.
FR4 Epoxy Sheet in Tomorrow's PCBs
Peering ahead, FR4 epoxy sheet could indeed shape the trajectory of eco-friendly PCBs. Drawing from our extensive experience at J&Q, including partnerships that span continents, we're optimistic about its adaptability. Let's explore the horizon.
Emerging Innovations and Adaptations
Innovators are reimagining FR4 epoxy sheet with bio-based resins from plant sources, slashing petroleum dependency while preserving robustness. Hybrid composites, blending FR4 with recycled polymers, are emerging to enhance flexibility for wearable tech. Additive manufacturing techniques now allow 3D-printed FR4 variants, enabling complex geometries that traditional laminates can't match, all with reduced material waste. Thermal management upgrades, like embedded graphene, dissipate heat more efficiently, extending device lifespans and cutting energy use in operation. These tweaks position FR4 as a frontrunner in next-gen PCBs, especially for IoT devices demanding compactness and eco-credentials.
Market Trends and Global Adoption
Globally, the PCB market is tilting green, with Asia-Pacific leading in halogen-free FR4 production due to stringent regulations. Demand surges in electric vehicles, where FR4's insulation supports high-voltage batteries sustainably. Market reports project a compound annual growth rate of over 5% for eco-friendly laminates through 2030, fueled by 5G and renewable energy booms. Our foreign trade expertise shows European and North American firms prioritizing suppliers with verified green credentials, boosting FR4's uptake. Collaborations between material scientists and electronics giants are accelerating standardization, making eco FR4 more accessible and affordable worldwide.
Challenges and Pathways Forward
Despite promise, hurdles like higher costs for halogen-free FR4 persist, though economies of scale are narrowing the gap. Supply chain vulnerabilities, from raw material sourcing to geopolitical tensions, demand diversified strategies. Performance in extreme environments requires ongoing R&D to match or exceed traditional versions. Pathways include government incentives for green tech and industry consortia sharing best practices. By addressing these, FR4 epoxy sheet can solidify its role, evolving from a reliable standard to a sustainable powerhouse in PCB innovation.
Conclusion
In wrapping up, FR4 epoxy sheet stands poised to influence eco-friendly PCBs significantly. Its blend of proven reliability and adaptive green features addresses pressing environmental needs without sacrificing functionality. As innovations unfold, from bio-resins to enhanced recycling, it bridges today's demands with tomorrow's sustainability goals. Challenges remain, but with collaborative efforts, FR4 could redefine industry standards. Embracing it means investing in a cleaner electronic future.
Contact Us
Ready to explore how FR4 epoxy sheet can elevate your projects? Reach out to our team at J&Q for expert insights and tailored solutions. Contact us at info@jhd-material.com - we're here to help with our 20+ years of insulating sheet expertise.
References
1. "Printed Circuit Board Materials Handbook" by Martin W. Jawitz.
2. "Eco-Friendly Electronics: Materials and Processes" edited by John A. Rogers.
3. "Flame Retardants for Plastics and Textiles: Practical Applications" by Edward D.
4. "Sustainable Materials for Next-Generation Electronics" by Veera Gnaneswar Gude.
5. "Advanced Composites in Electronics" by Michael Pecht.
6. "Global PCB Market Report: Trends and Forecasts" by Prismark Partners LLC.